Testing Locations
Learn more about our locations and their certifications.
Study Outline
In the Antibiotic Potency test procedure, cultures are grown and adjusted using turbidimetric measurement techniques. An aliquot of the adjusted culture is added to a thin layer of agar to create a seed layer. Test samples are diluted to an appropriate test concentration according to labeled potency claims. A reference standard antibiotic is diluted in a similar manner with several dilutions used to create a standard curve.
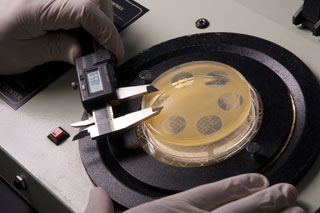
For each sample tested, three plates are used. Six stainless steel penicylinders are placed on each plate so that they are at approximate 60° intervals with a center spacing of approximately 5 cm. Three cylinders are filled with the median dilution standard and three cylinders are filled with the sample. The plates are incubated and zones of inhibition are measured with calibrated calipers sensitive to 0.01 mm.
A standard curve is prepared the day of testing. For the standard curve, three plates are prepared for each of four concentrations that bracket the median test dilution. Six cylinders are placed on each plate so that they are at approximate 60° intervals with a center spacing of approximately 5 cm. Three alternate cylinders are filled with the median test dilution and the other three cylinders are filled with the dilution concentration of the standard curve. The plates are incubated and the observed zones of inhibited growth are measured with calibrated calipers sensitive to 0.01 mm.
The measured zone values are entered into a validated spreadsheet for zone diameter correction, linear regression output, and potency calculations. Using a log transformation straight line method with the least squares fitting procedure, a reference point can be interpolated. Log-linear regression is used to compute an R2 value to estimate linearity.
The sample potency is estimated by averaging the reference standard zone diameters and the sample zone diameters on the three plates used. Concentrations are calculated from the corresponding corrected values of zone diameters. The log value is converted to the antilog. The antilog value is multiplied by the dilution factor to obtain the concentration in mg/mL of active antibiotic. These calculations are done with a validated spreadsheet for antibiotic potency.
If you have additional questions about Antibiotic Potency tests, or would like to consult with the experts at Nelson Labs, just send us a request or call us at +1 (801) 290-7500.